Gateway Instances in Rackspace Cloud¶
A Gateway Instance is a Rackspace Cloud Server that routes traffic between the public internet and any other Rackspace Cloud Servers that do not have a public IP. A Gateway Instance is typically a virtual network appliance.
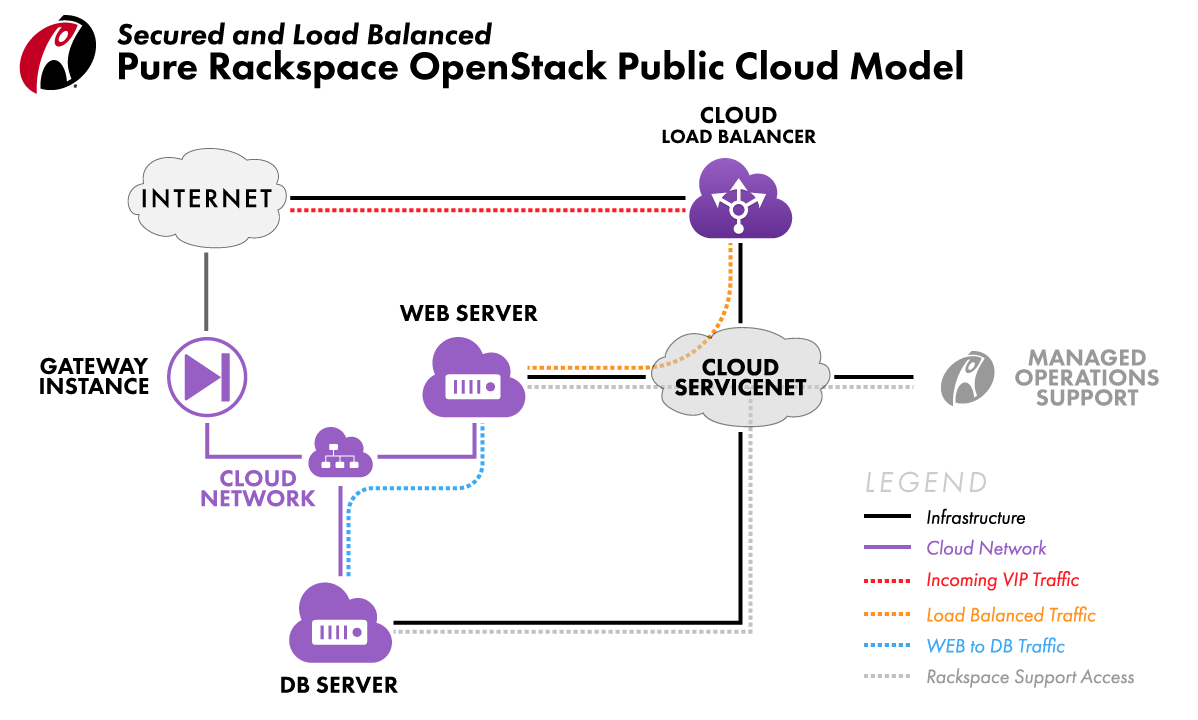
In the diagram below, the web server and database server do not have PublicNet attached. Instead, their outbound internet access is routed through the Gateway Instance by using Cloud Networks. This reduces exposure to attackers.
The web server also has public-facing services exposed by using a Cloud Load Balancer, which connects over ServiceNet.
Creating a Gateway Instance in Rackspace Cloud¶
From the Cloud Control Panel, navigate to Servers > Create Resources. On the Create Server page, choose a virtual network appliance image, such as the Fortinet Fortigate-VM. Under Advanced Options, ensure that Configure as Gateway is checked (as it is by default).
After the server is built, Rackspace’s post-build automation software (ServerMill) automatically performs all steps described in the section entitled “How to set up Internet access for servers without PublicNet or ServiceNet” within the Building servers without PublicNet or ServiceNet section of this guide.
Note
You can also use these Cloud Orchestration templates, which create the Gateway Instance and a Cloud Network with all needed configuration at the same time.
Building Servers Behind Your Gateway Instance¶
On the Cloud Control Panel server creation page, scroll down to Advanced Options.
Click Select Networks and uncheck PublicNet.
Select the Cloud Network that has the name of your Gateway Instance.
- Optional Enable ServiceNet if you use Rackspace products
such as Cloud Backups or Cloud Files.
Click Create Server. The server builds without a public IP address. However, since NAT is configured on the Gateway Instance, the server can connect outbound to the Internet.
Accessing Servers Behind Your Gateway Instance¶
You can access servers behind the FortiGate-VM in a variety of ways:
Using the Gateway Instance to forward remote access ports to the server behind the Gateway Instance.
Configuring VPN on the Gateway Instance, then connecting to VPN. Once connected to VPN, you can access servers across the VPN via their Cloud Networks (private) IP addresses.
Using the Emergency Console available on the Server Details page in the Cloud Control Panel.